Flame Resistant
The characteristic of a fabric to resist ignition and to self extinguish if ignited
Summary of Flame Resistant Clothing
- Does not ignite and burn, melt or drip
- Maintains a barrier
- Insulates the wearer from heat
- Resists breaking open
- Reduces burn injury and increases chances of survival
Proper Use of Flame Resistant Garments
- Appropriate to the hazard
- Always the outermost layer
- Worn correctly; zipped, buttoned, etc.
- All natural, non-melting undergarments
- Clean, no flammable contaminants
- Repaired correctly and removed from service when needed
Arc Flash
An arc flash is the light and heat produced from an electrical arc supplied with sufficient electrical energy to cause substantial damage, harm, fire or injury.
With increased awareness of the dangers of arc flash, the materials are tested for their arc rating. The arc rating is the maximum incident energy resistance demonstrated by a material prior to break open (a hole in the material) or necessary to pass through and cause with 50% probability a second or third degree burn.
Among the best fabrics for protection against electrical arc flash are the Modacrylic-cotton blends.
Arc ratings
Arc rating is normally expressed in cal/cm² (or small calories of heat energy per square centimeter) also known as ATPV(arc thermal protective value).
The tests for determining arc rating are defined in: ASTM F1506, titled Standard Performance Specification for Flame Resistant Textile Materials for Wearing Apparel for Use by Electrical Workers Exposed to Momentary Electrical Arc and Related Thermal Hazards, is a standard of the American Society for Testing & Materials (ASTM).
ASTM F1891, Arc Standard for Flame Resistant Rainwear
Example:
Meets ASTM F1506
Arc Rating: ATPV = 26 cal/cm²
NFPA70E and HRC
NFPA 70E, titled Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace, is a standard of the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA).
The document covers electrical safety requirements for industrial personnel (for example: electricians, maintenance workers, operators).
The NFPA is best known for its sponsorship of the National Electrical Code (NEC).
HRC (hazard/risk category) is used to determine the necessary arc rating of a garment worn during a given job task. The classification of the listed task according to the type of hazard present when performing the task. Zero represents minimal risk, four represents the greatest risk.
NFPA 70E Hazard/Risk Categories (HRC)
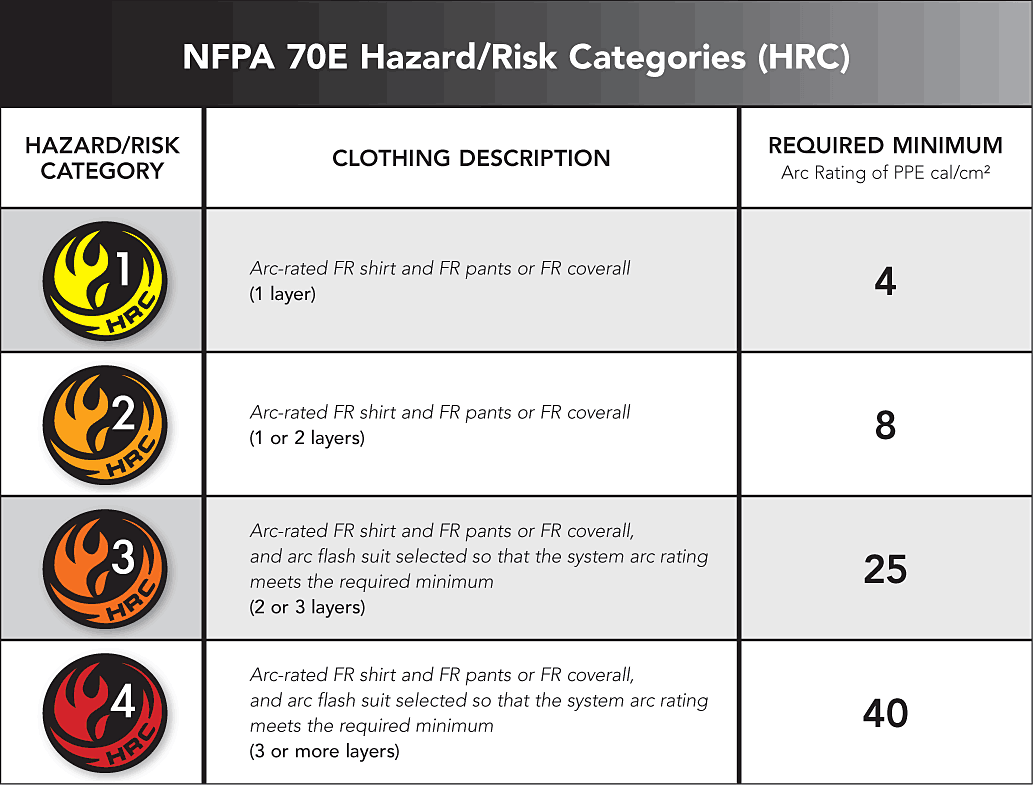
Example:
Arc Rating: ATPV = 26 cal/cm²
NFPA 70E / HRC = 3
Many organizations have adopted NFPA 70E, requiring employees to wear the appropriate HRC level garments for the type of work performed.
Flash Fire
A flash fire is a sudden, intense fire caused by ignition of a mixture of air and a dispersed flammable substance such as a solid (including dust), flammable or combustible liquid (such as an aerosol or fine mist), or a flammable gas. It is characterized by high temperature, short duration, and a rapidly moving flame front.
NFPA 2112 – Standard for FR Garments for Protection Against Flash Fire
ASTM F2733 – Standard for FR Rainwear for Protection Against Flame Hazards
OccuNomix FR Products that meet the standards:
NFPA 2112 – FR Coveralls (Nomex & Indura fabrics)
ASTM F2733 – FR Rainwear (jacket & bib pants)
Flame Resistant Fabrics
Flame resistant fabrics can generally be divided into two groups:
- Treated: Applied chemical treatment
- Fabric made of natural fiber
- Flame resistant treatment applied
- Guaranteed FR for the life of the garment provided that laundering guidelines are followed
- No bleach
- No fabric softener
- No starch
- Inherent: Essential characteristic
- Synthetic fibers synthesized to have permanent FR properties
- Guaranteed FR for the life of the garment provided that laundering guidelines are followed
- No bleach
- No fabric softener
- No starch
- Color change does not indicate reduced FR performance
Advantages/Disadvantages – there is no perfect fabric